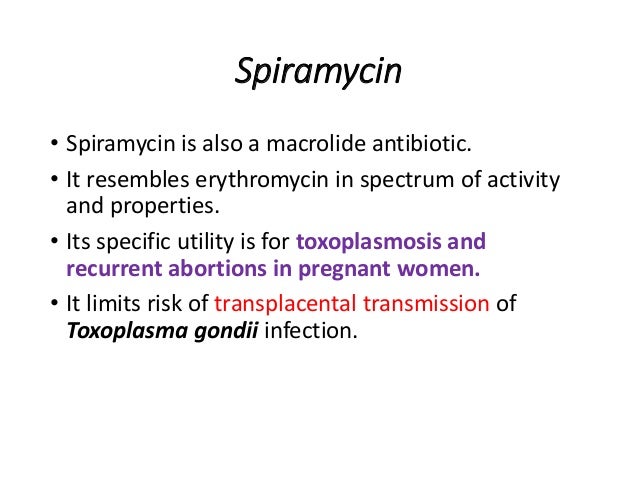
Antibiotics Classification, Synergism And Antagonism Dr Naeem Tahir Area Sales Manager Jadeed Farms (pvt) ltd By 2 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Takes advantage of the biochemical differences between microorganisms and host cells Antimicrobial drugs are effective in the treatment of infections because of their selective toxicity TheSpiramycin 15million Tablets About Spiramycin Macrolide Antibiotic, Antibacterial (systemic,antiprotozoal,In toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidiosis Mechanism of Action of Spiramycin Spiramycin is a member of macrolide antibiotic It binds to the 50S sub unit of bacterial ribosome and inhibits translocationie they interfere with the transfer of the newly formed peptide chainSpiramycin is used to treat many kinds of infections It is often used to treat toxoplasmosis in pregnant women since spiramycin decreases the chance that the unborn baby will get the infection Spiramycin may also be used for other problems as determined by your doctor It will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infections
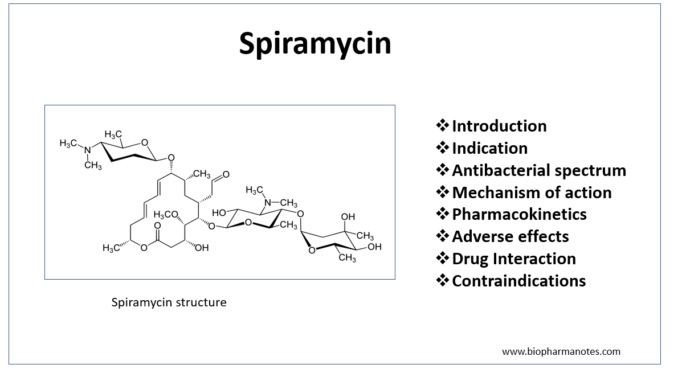
Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes
Mechanism of action of spiramycin and other macrolides
Mechanism of action of spiramycin and other macrolides- It has been suggested that these compounds block the path by which nascent peptides exit the ribosome We have studied the mechanisms of action of four macrolides (erythromycin, josamycin, spiramycin and telithromycin), one lincosamide (clindamycin) and one streptogramin B (pristinamycin IA)22 (Suppl B)13–23 Chamberland S, Kirst HA, Current WL
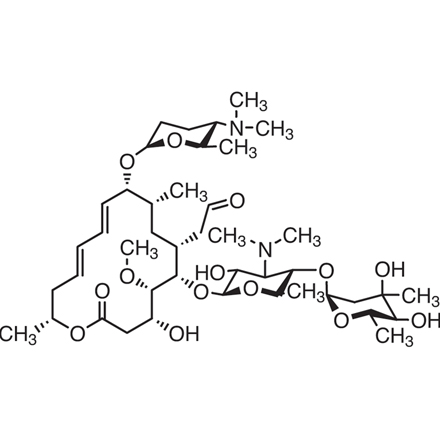



Spiramycin 8025 81 8 Tci Chemicals India Pvt Ltd
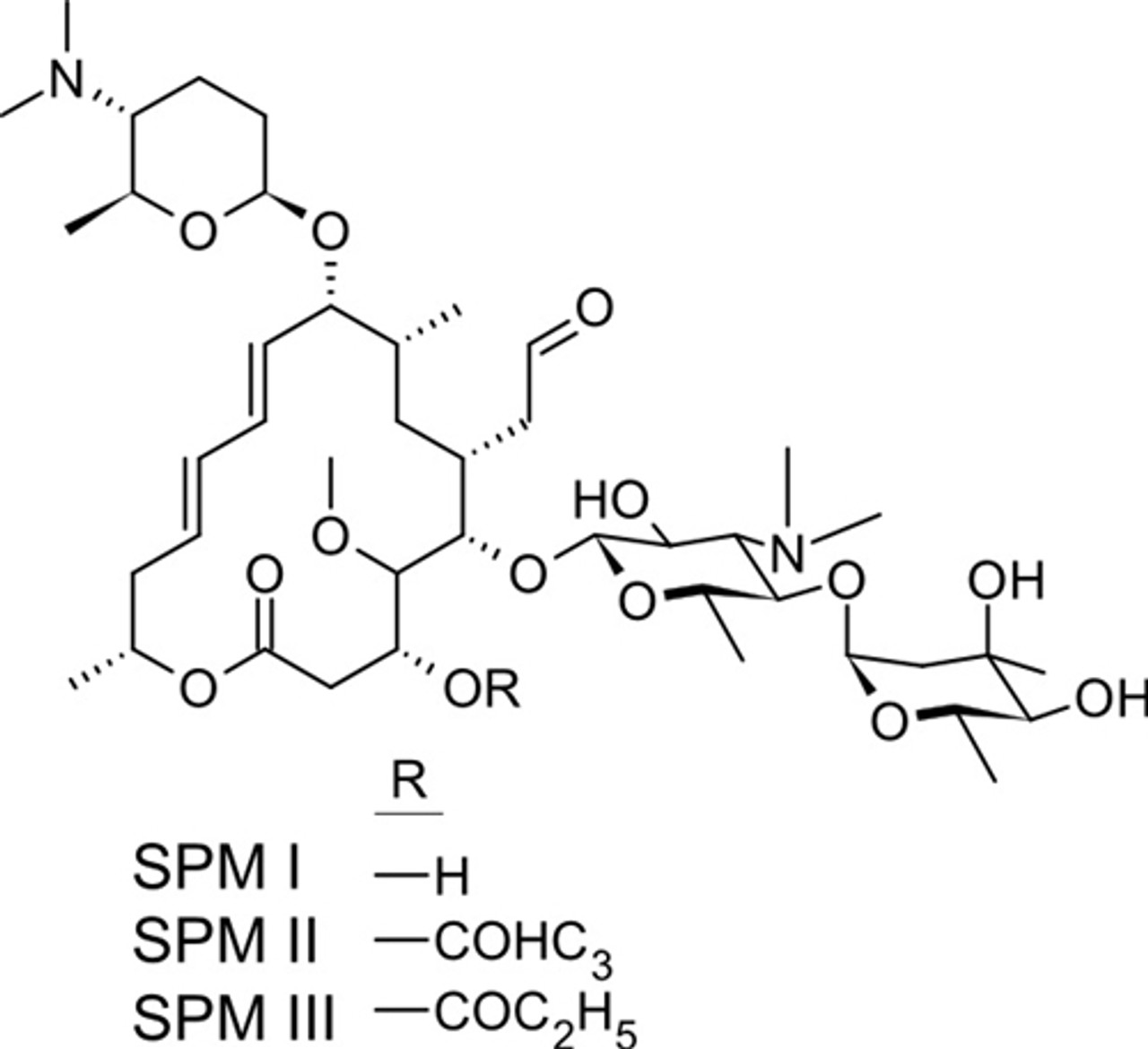
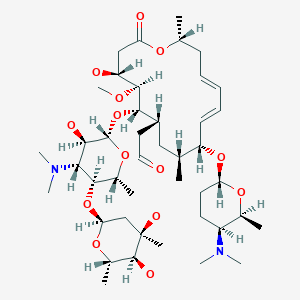
Spiramycin is a broadspectrum 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic composed of a mixture of spiramycin I, II, and III Spiramycin was first isolated by PINNERTSINDICO in 1954 from Streptomyces ambofaciens Spiramycin is a bacterial protein synthesis inhibitor, it works by irreversibly binding to the Psite on the 50s ribosome, preventing peptide bond formation andThe similarity between these mechanisms and their relation to the general mode of macrolide action is discussed and the discrepancies between currently available data are highlighted Key words macrolides, erythromycin, ketolides, azithromycin, clarithromycin, tylosin, carbomycin, spiramycin, ribosome, resistance INTRODUCTIONAlthough the exact mechanism of action is unclear, artemisinins appear to act as prodrugs that are metabolized by target cells to produce reactive oxygen species When toxicity is a concern, spiramycin, a macrolide protein synthesis inhibitor, is typically administered for the treatment of
The mechanism of action of macrolides is inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis, and they are thought to do this by preventing peptidyltransferase from adding the growing peptide attached to tRNA to the next amino acid (similarly to chloramphenicol) as well BackgroundThe mechanisms underlying the nonantimicrobial immunomodulatory properties of macrolides are not well understoodObjectivesTo systematically review the evidence for the immunomodulatory properties of macrolides in humans and to describe the underlying mechanism and extent of their influence on the innate and adaptive immune systemMethodsAAlthough its mechanism of action is not fully defined, it is believed to act as an inhibitor of protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes
The similarity between these mechanisms and their relation to the general mode of macrolide action is discussed and the discrepancies between currently available data are highlighted Keywords macrolides , erythromycin , ketolides , azithromycin , clarithromycin , tylosin , carbomycin , spiramycin , ribosome , resistanceSpiramycin I is a macrolide antibiotic and antiparasitic Mechanism of Action & Protocol Mechanism of antiplasmodial action In bacteria, macrolides inhibit the synthesis of cell proteins through binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome The inhibition of protein synthesis through the inhibition of transpeptidation explains the



2



Macrolides Antibiotics With Lincosamide
The similarity between these mechanisms and their relation to the general mode of macrolide action is discussed and the discrepancies between currently available data are highlighted Keywords macrolides, erythromycin, ketolides, azithromycin, clarithromycin, tylosin, carbomycin, spiramycin, ribosome, resistanceMacrolides have been used in the treatment of infectious diseases since the late 1950s Since that time, a finding of antagonistic action between erythromycin and spiramycin in clinical isolates1 led to evidence of the biochemical mechanism and to the current understanding of inducible or constitutive resistance to macrolides mediated by erm genes containing, respectively, the1 Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jun;94(6) The mechanism of action of antibiotics, particularly spiramycin Article in French VIDEAU D



1




Spira Plus Spiramycin Rooyan Darou
8 Peptide Antibiotics Peptide Antibiotics are drugs with polypeptides structure Subgroup of Peptide Antibiotics Polymyxins Glycopeptides Bacitracin Streptogramins Each drug group has its own mechanism of action 4 groups and 4 mechanism GKM/BIO319Antibiotics/Lec 8 03/Sem02/13 9Spiramycin is produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens It is a mixture of compounds, similar in their elementary composition as well as in their physical, chemical, and bacterial properties Its antibacterial spectrum includes mainly Grampositive organismsSpiramycin (Rovamycin) is a macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens with against bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii activities, and also has antiparasitic effect Spiramycin is composed of a 16member lactone ring, on which three sugars (mycaminose, forosamine, and mycarose) are attached Mechanism of Action & Protocol




Adsorption Of Metronidazole And Spiramycin By An Algerian Palygorskite Effect Of Modification With Tin Sciencedirect



2
Chemical formula C43H74N2O14 Drugbank ID DB ATC code(s) J01FA02, J01RA04 Chemical structure of spiramycin Click to enlargeStopping therapy too soon may result in a reinfection SIDE EFFECTS Indigestion, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or stomach ache may occur If any of these effects continue or become bothersome, inform your doctor In the unlikely event you have an allergic reaction to this drug, seek medical attention immediatelySpiramycin is available only with your doctor's prescription Before Using In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the good it will do This is a decision you and your doctor will make For this medicine, the



Frontiers A Systematic Review Of In Vitro And In Vivo Activities Of Anti Toxoplasma Drugs And Compounds 06 16 Microbiology
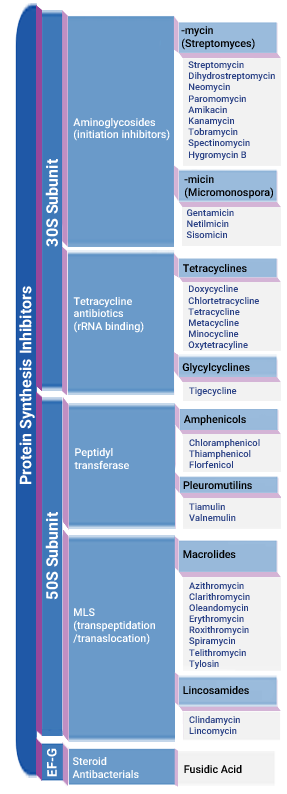



Antibiotic Classification Table
It has a role as an antitussive, an opioid analgesic, a muopioid receptor agonist and a drug allergen It is an organic heteropentacyclic compound and a morphinane alkaloid Pholcodine formula is 3omorpholinoethylmorphine and it is classified as an antitussive which isThe macrolide antibiotics (eg erythromycin, tylosin, spiramycin) are a structurally similar group of primarily bacteriostatic compounds Most drugs in this class were isolated from soil bacteria of the genus Streptomyces but anthelmintic drugs are diverse in their structures and mechanisms of action (Barragry, 1984b;BergogneBérézin E Spiramycin concentrations in the human respiratory tract a review J Antimicrob Chemother 19 Jul;



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html



Rovamycin 1 5million Tablets Rosheta
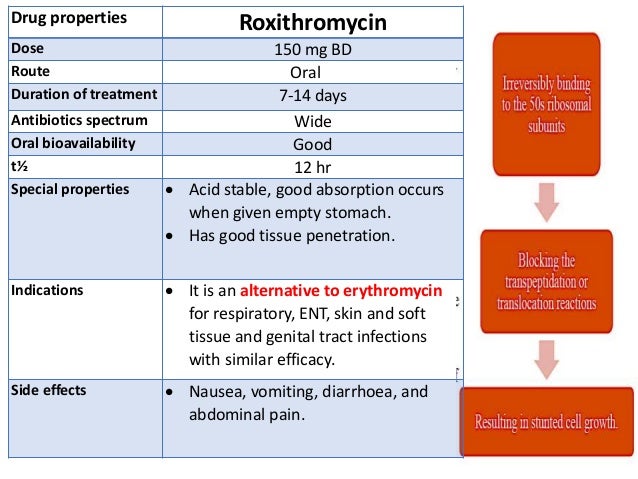
Mechanism of action In order to replicate, bacteria require a specific process of protein synthesis, enabled by ribosomal proteins 9 Erythromycin acts by inhibition of protein synthesis by binding to the 23S ribosomal RNA molecule in the 50S subunit of ribosomes in susceptible bacterial organismsMechanism of action Spiramycin is a macrolide antibacterial that inhibits protein synthesis by irreversibly binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosomal subunit thus blocking the transpeptidation or translocation reactions of susceptible organisms resulting in stunted cell growthAlthough the exact mechanism of action is unclear, artemisinins appear to act as prodrugs that are metabolized by target cells to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) When toxicity is a concern, spiramycin, a macrolide protein synthesis inhibitor, is typically administered for the treatment of



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Spiramycin Tablets
The mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 1 1 stoichiometry This antibiotic is a potent inhibitor of the binding to the ribosome of both donor and acceptor substratesSpiramycin can also be used to treat infections caused by other kinds of bacteria However, it is not routinely used because many diseasecausing bacteria has acquired resistance to it Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic, and it belongs to the same class with the antibiotics Erthromycin, Azithromycin, and TelithromycinMechanism of action Erythromycin displays bacteriostatic activity or inhibits growth of bacteria, especially at higher concentrations 28 By binding to the 50s subunit of the bacterial rRNA complex, protein synthesis and subsequent structure and function processes critical for life or replication are inhibited 28




14 And 15 Membered Lactone Macrolides And Their Analogues And Hybrids Structure Molecular Mechanism Of Action And Biological Activity Sciencedirect




Erythromycin Wikipedia
Unlike Penicilline, that directly kills the bacteriamembrane and works therefore bactericidal, spiramycin has a growthinhibiting effect and acts primarily bacteriostatic It is especially working against bacteria with an active metabolism Inactive bacteria are merely adequately affected The range of the pathogens for spiramycin and most of the macrolides are grampositive cocci, rodMechanism of Action of Metronidazole Metronidazole is nitro imidazoles which have broad spectrum cidal activity against Protozoa and some anaerobic bacteria Its selective toxicity to anaerobic microbes involves 1 Drug enters the cell by diffusion, 2 • Spiramycin † • Pyrimethamine The sites and mechanisms of action of selected antiparasitic drugs are depicted in Figure 441 F IGURE 441 Sites of action and mechanisms of antiparasitic drugs The sites and mechanisms of antiparasitic agents include cell membranes and ion channels, energy metabolism enzymes, cytoplasmic microtubules



Spiramycin Drug Monograph Druginfosys Com
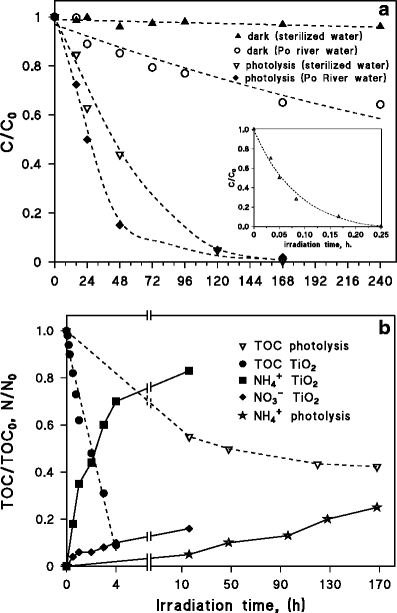



Fate Of Antibacterial Spiramycin In River Waters Springerlink
Spiramycin Mechanism Spiramycin is an antibacterial drug used in the treatment of toxoplasmosis in children as well as in pregnant women Indication Toxoplasmosis;Mechanism of action Macrolides act at the ribosomal level, specifically on the 50S subunit, blocking its action By doing this, they inhibit the protein synthesis of sensitive microorganisms without affecting the ribosomes of mammals This effect manages to prevent the growth of bacteria Due to their mechanism of action, macrolides are22 (Suppl B)117–122 BrissonNoël A, TrieuCuot P, Courvalin P Mechanism of action of spiramycin and other macrolides J Antimicrob Chemother 19 Jul;




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar



2
In 12 surveys, T gondii mutants were identified as a good model to study mechanisms of resistance and drug target in parasites Interestingly, analogous amino acid substitutions in the Toxoplasma enzyme identified to confer PYR resistance Moreover, resistance to clindamycin, spiramycin and azithromycin is encoded in the rRNA genes of T gondiiContraindications Hypersensitivity to any component of product Dosing 2 The Mechanism of Antibacterial Action of Macrolides Macrolide antibiotics have been used for many years to treat infectious diseases Macrolides antibacterial mechanism of action involves binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, which causes inhibition of the biosynthesis on ribosomal protein level 1, 2Both macrolides and ketolides bind domain V of 23S ribosomal RNA



Macrolides Antibiotics With Lincosamide



Spiramycin Toku E
Spiramycin is a macrolide originally discovered as product of Streptomyces ambofaciens, with antibacterial and antiparasitic activities Although the specific mechanism of action has not been characterized, spiramycin likely inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosomeSpiramycin Tablet Working, Mechanism of Action and Pharmacology Spiramycin Tablet improves the patient's condition by performing the following functions Inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis Spiramycin Tablet Composition and Active Ingredients Spiramycin Tablet is composed of the following active ingredients (salts) Spiramycin (15 MG)Mode of action Inhibition of protein synthesis Macrolides reversibly bind to 50S subunit of the ribosomes and inhibit transpeptidation and translocation processes, resulting in premature detachment of incomplete polypeptide chains Examples Macrolides approved for veterinary use Erythromycin, Tylosin, Spiramycin, Tilmicosin, Tulathromycin




Spiramycin 8025 81 8 Tci Chemicals India Pvt Ltd




Tetracycline Antibiotics Wikipedia
Macrolides are generally bacteriostatic, although some of these drugs may be bactericidal at very high concentrations The mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 11 stoichiometry



Spiramycin Adsorption Behavior On Activated Bentonite Activated Carbon And Natural Phosphate In Aqueous Solution Springerlink




Remarkable Histopathological Improvement Of Experimental Toxoplasmosis Treated With Spiramycin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Research Square




Remarkable Histopathological Improvement Of Experimental Toxoplasmosis Treated With Spiramycin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Research Square



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Clinical Microbiology And Infection



Spiramycin Wikipedia




Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes



Spiramycin Toku E




Spiramycin Vetranal Analytical Standard 8025 81 8 Sigma Aldrich




Spiramycin New Drug Approvals
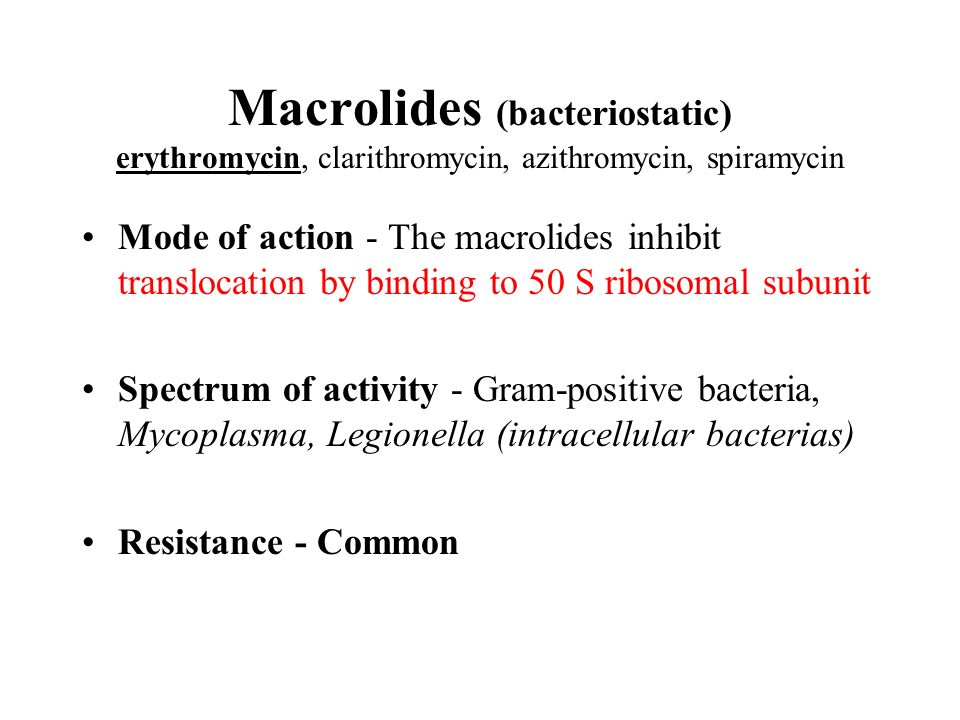



Prof Khaled H Abu Elteen Ppt Download



2
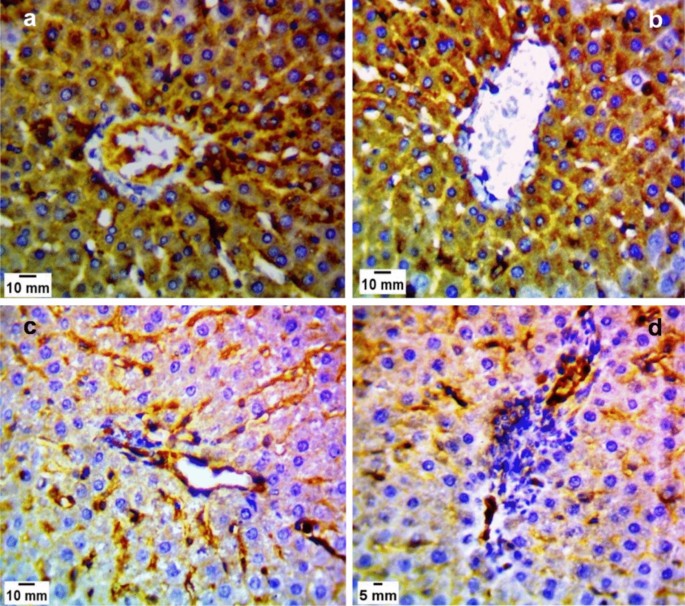



Effect Of Spiramycin Versus Aminoguanidine And Their Combined Use In Experimental Toxoplasmosis Springerlink




Oxytetracycline Wikipedia



Pharmacokinetics Of Spiramycin In The Rhesus Monkey Transplacental Passage And Distribution In Tissue In The Fetus Abstract Europe Pmc




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




The Binding Site Of Blasticidin S And Spiramycin On The 50 S Ribosomal Download Scientific Diagram




How Macrolide Antibiotics Work Trends In Biochemical Sciences
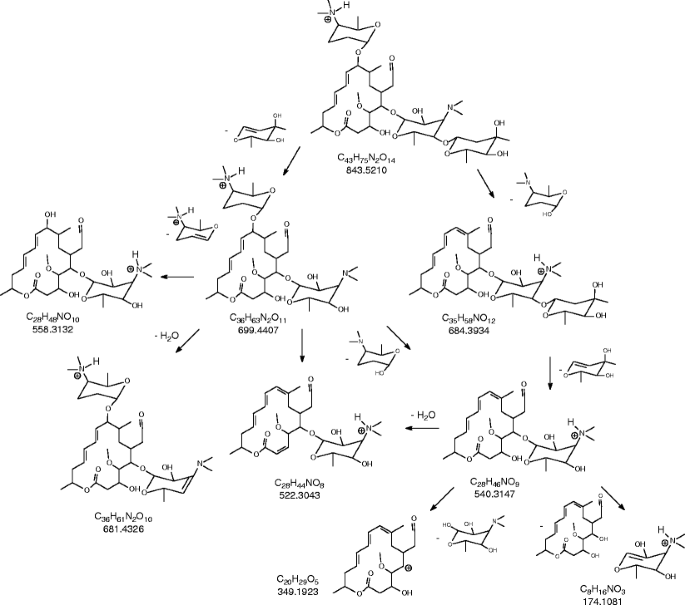



Fate Of Antibacterial Spiramycin In River Waters Springerlink



Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier India Buy Online




Effect Of Nitazoxanide And Spiramycin Metronidazole Combination In Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis Sciencedirect



2




Spiramycin Toku E




Polyamines Affect Diversely The Antibiotic Potency Journal Of Biological Chemistry
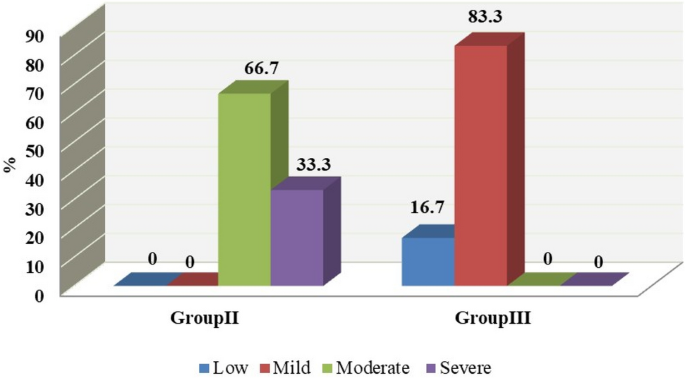



Effect Of Spiramycin Versus Aminoguanidine And Their Combined Use In Experimental Toxoplasmosis Springerlink



Spiramycin 3million Tablets Rosheta




Figure 1 From The Mechanism Of Action Of Macrolides Lincosamides And Streptogramin B Reveals The Nascent Peptide Exit Path In The Ribosome Semantic Scholar
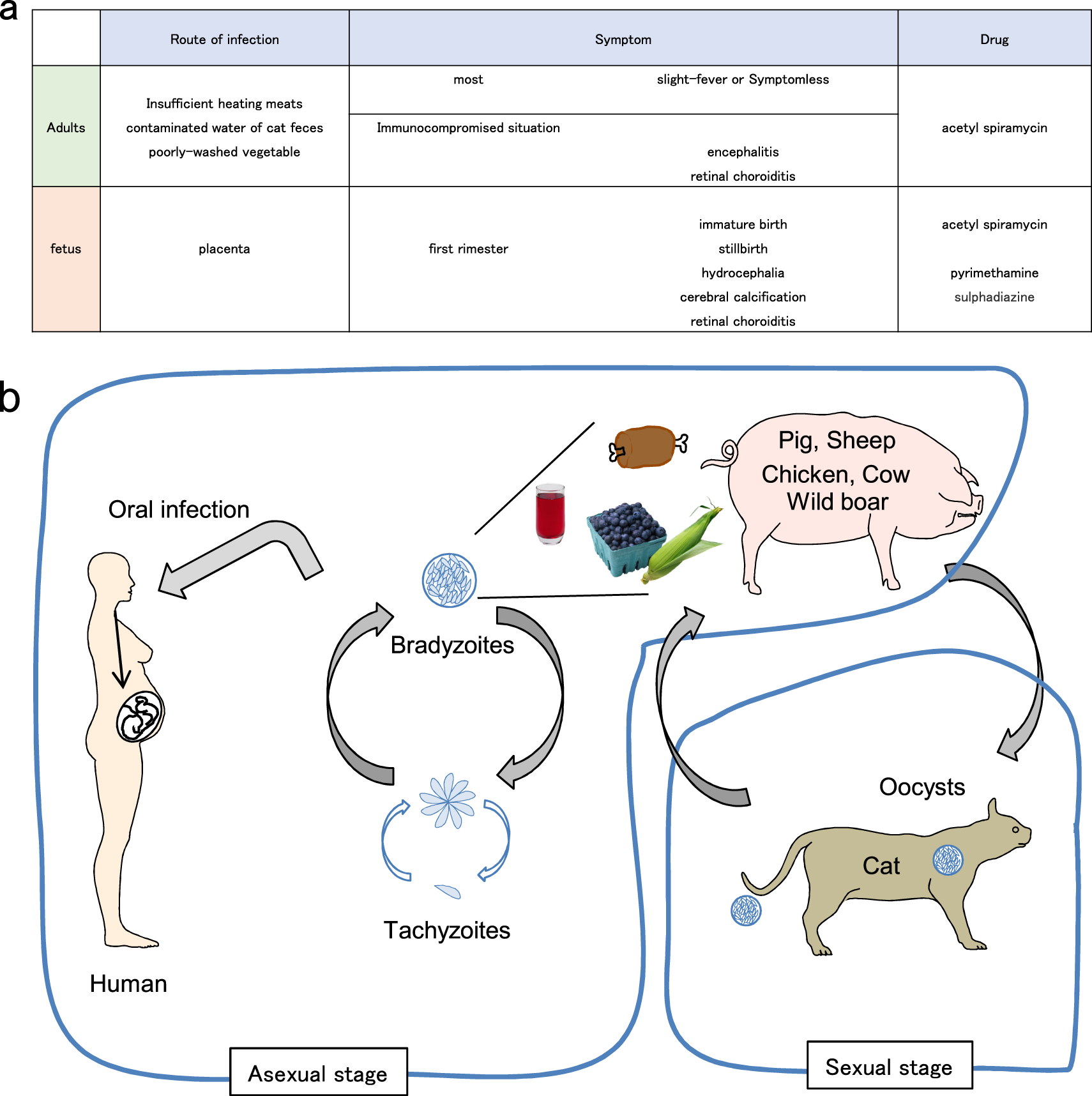



Innate Adaptive And Cell Autonomous Immunity Against Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Experimental Molecular Medicine



2



2




Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier Exporter



Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier Exporter From India
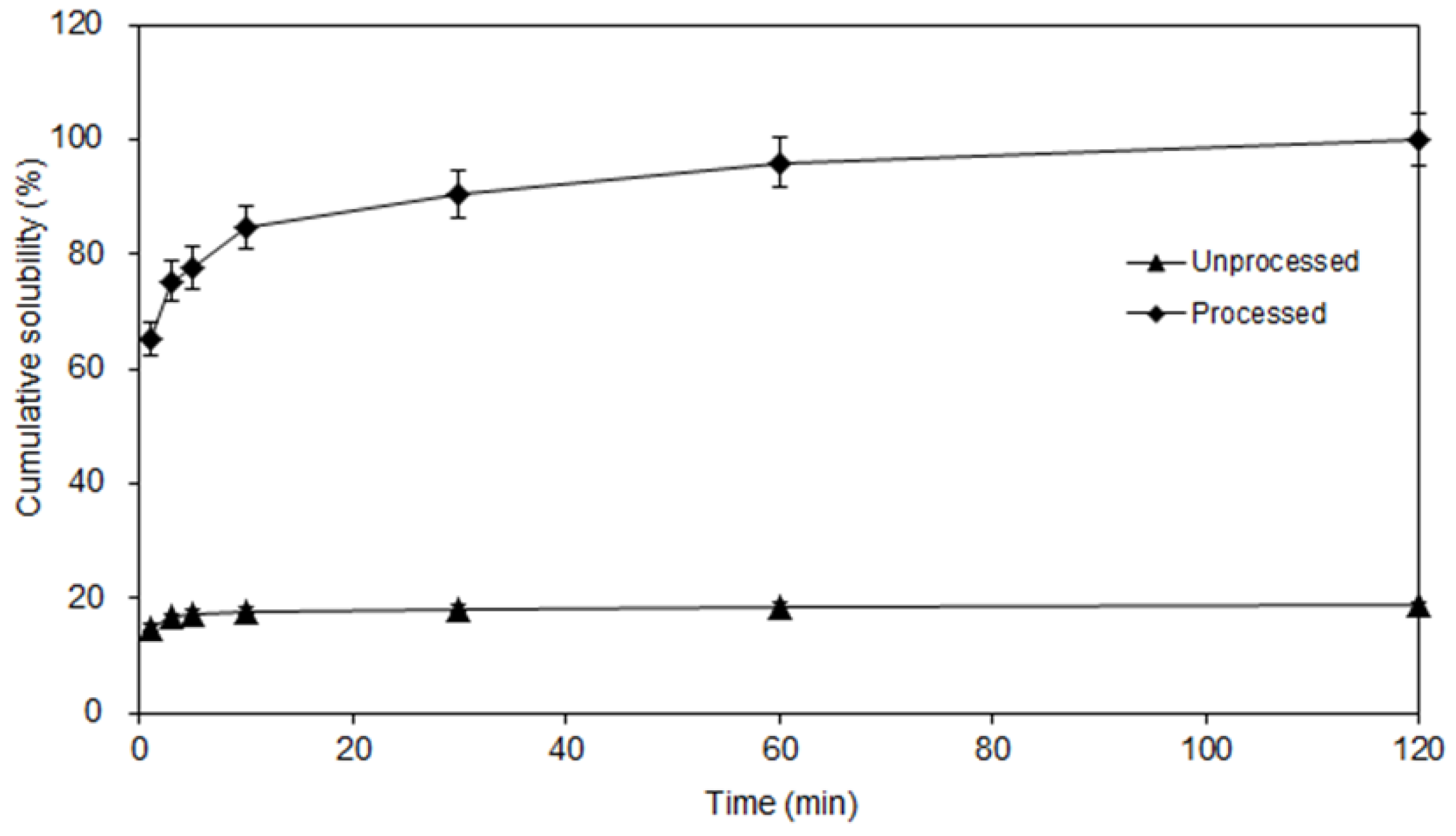



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html
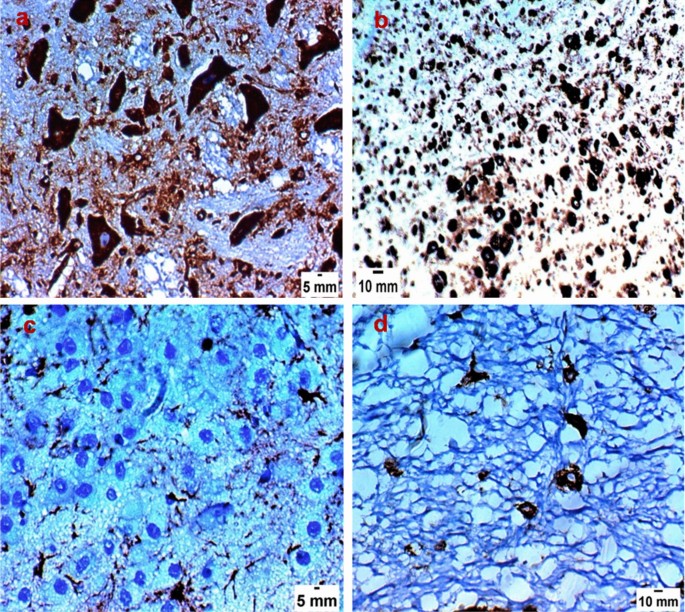



Effect Of Spiramycin Versus Aminoguanidine And Their Combined Use In Experimental Toxoplasmosis Springerlink




Inhibitory Effect Of Spiramycin On Lipid Accumulation In 3t3 L1 Download Scientific Diagram
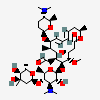



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
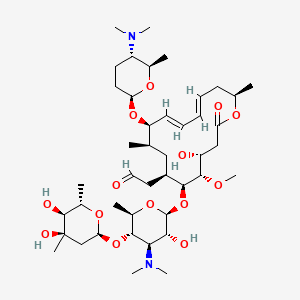



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
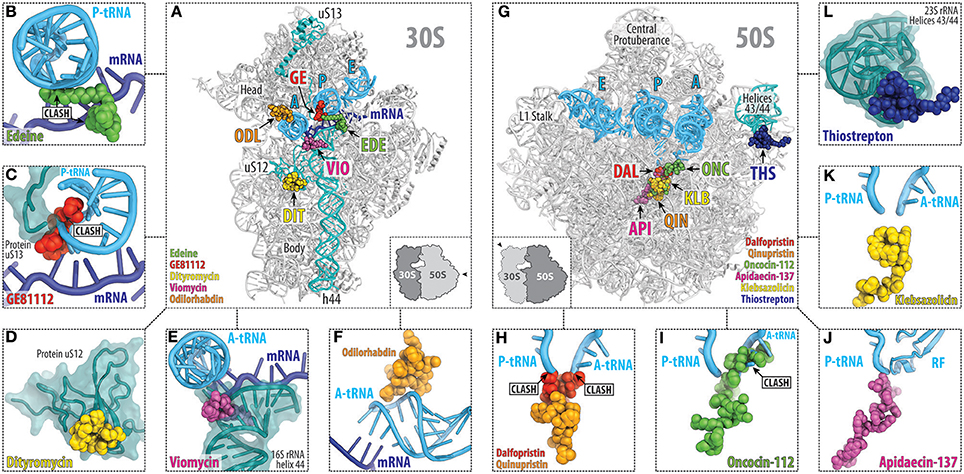



Frontiers The Mechanisms Of Action Of Ribosome Targeting Peptide Antibiotics Molecular Biosciences



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Spiramycin Rovamycine Macrolide Antibiotic Cas 8025 81 8 Ab Abcam




Medical University Of Sofia Faculty Of Me Department
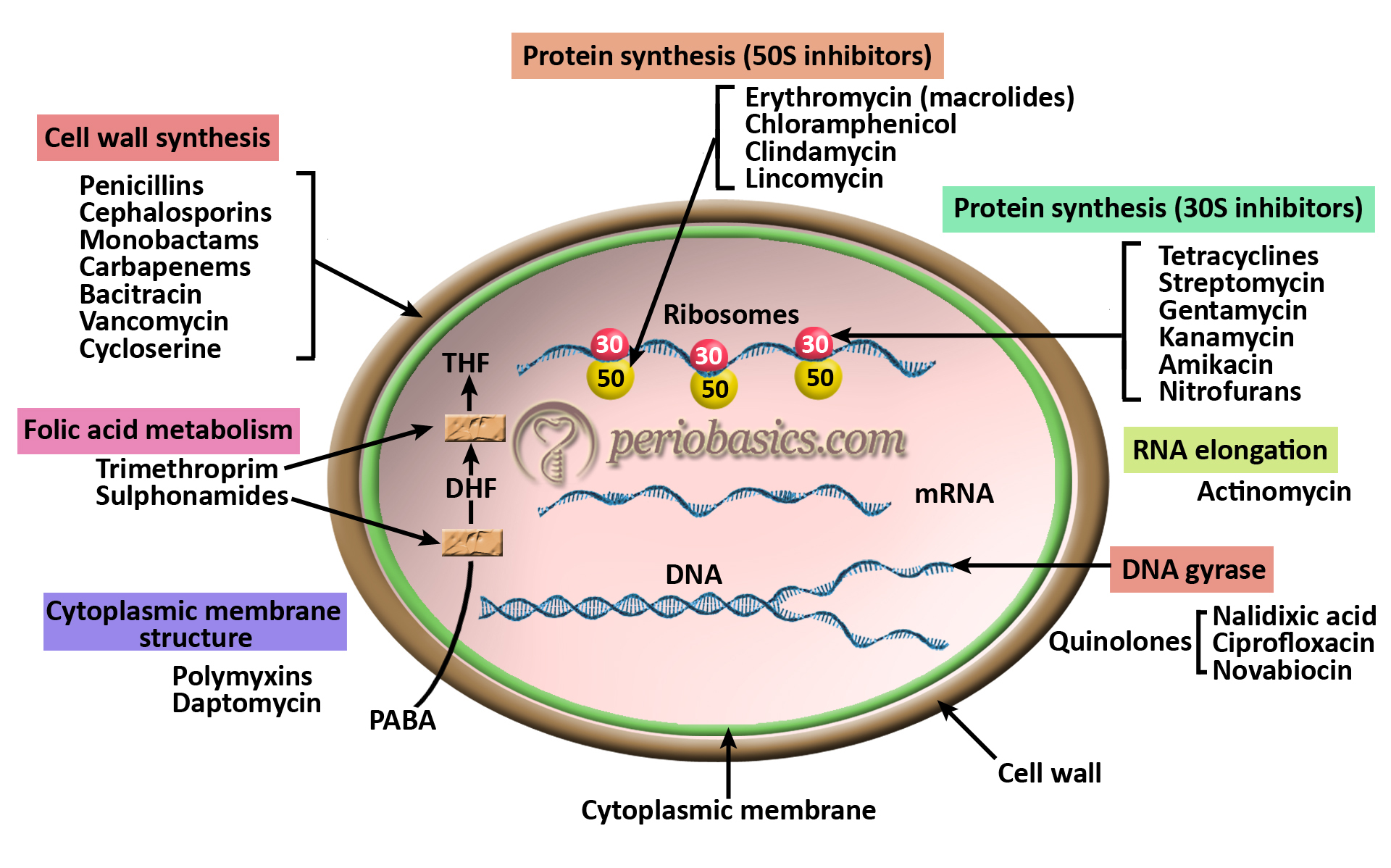



Chemotherapeutic Agents Used In Periodontics Periobasics Com
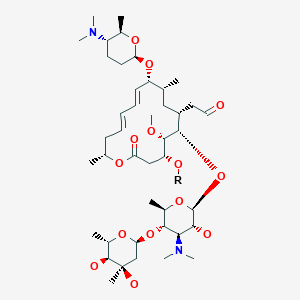



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals
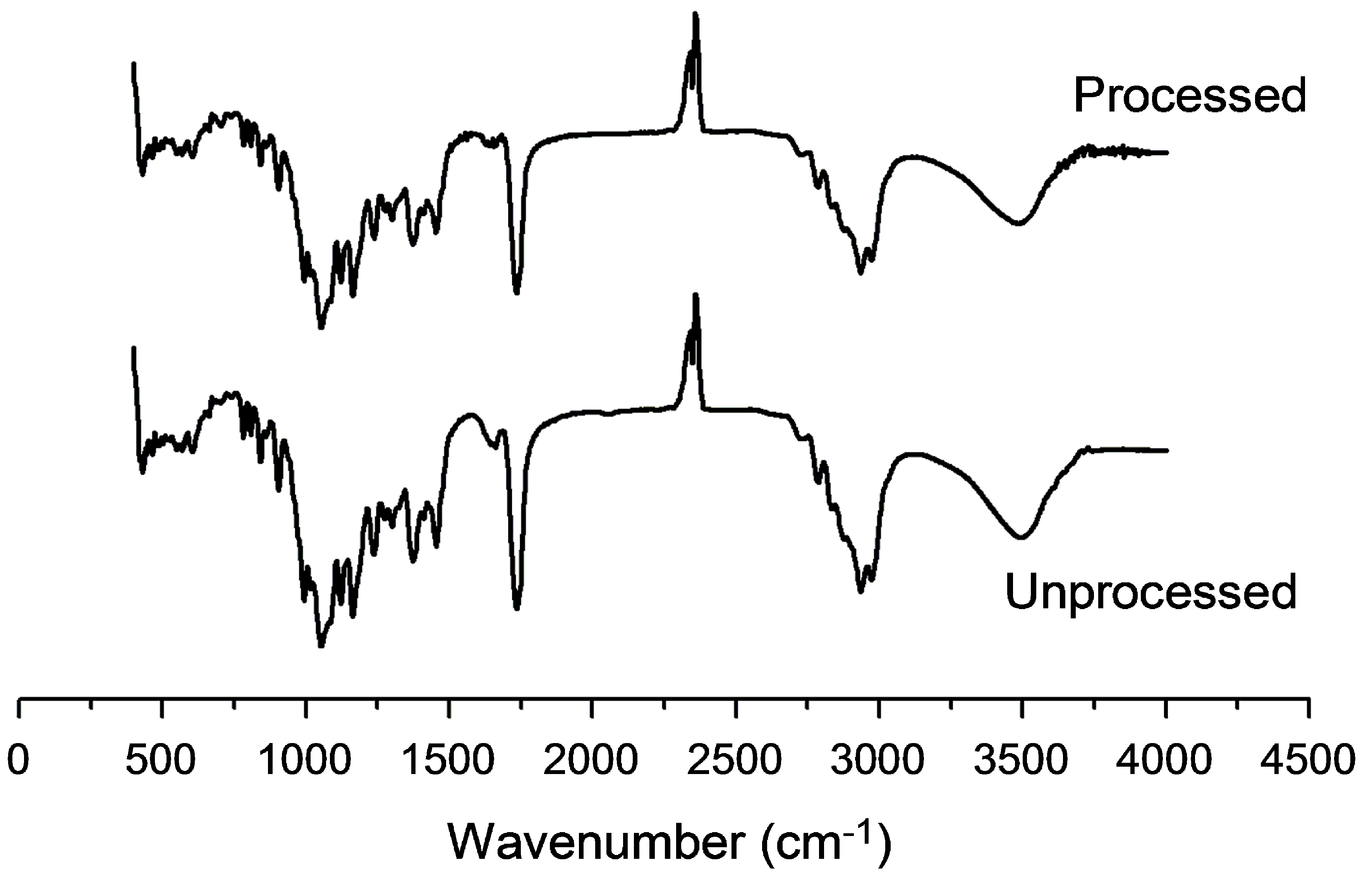



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html



1




Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acid Synthesis And Metabolism Ppt Download
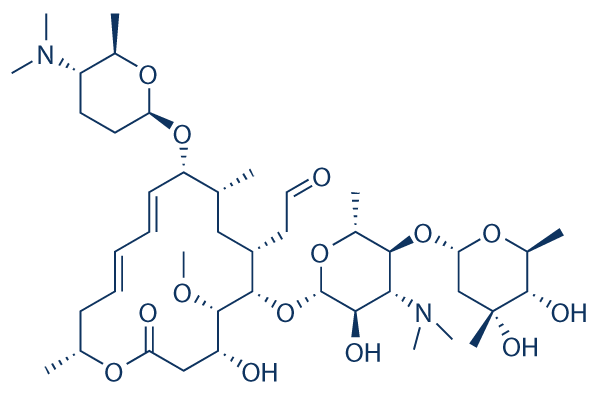



Spiramycin 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical



2




Spiramycin Tablets Supplier Manufacturer Exporter India




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar




Stylized Cells Depicting The Transport Metabolism And Mechanism Of Download Scientific Diagram



Rovamycin 3million Tablets Rosheta




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Minimum Influent Concentrations Of Oxytetracycline Streptomycin And Spiramycin In Selecting Antibiotic Resistance In Biofilm Type Wastewater Treatment Systems Sciencedirect



2



Acetyl Spiramycin Tablet Beijingyaowuyanjiuyuan



2
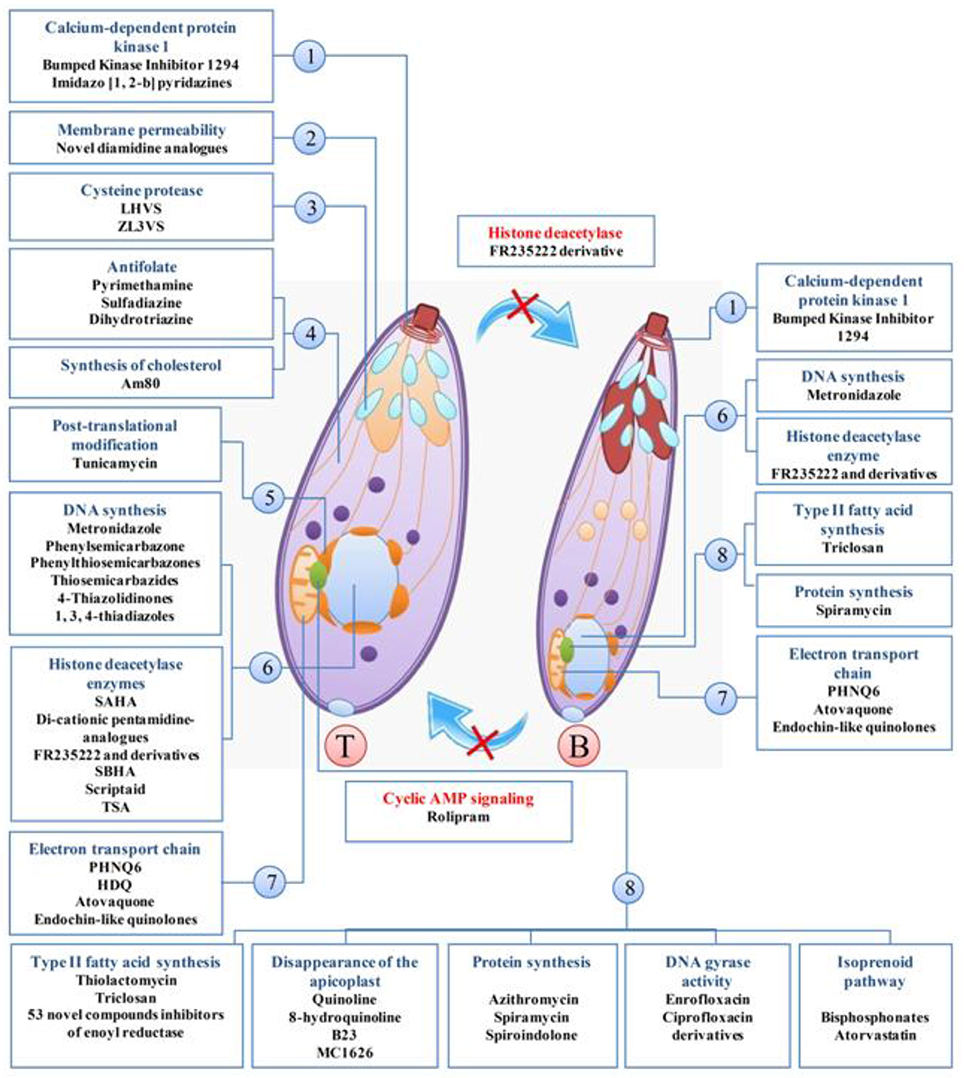



Frontiers A Systematic Review Of In Vitro And In Vivo Activities Of Anti Toxoplasma Drugs And Compounds 06 16 Microbiology




Pdf Nonoptimal Microbial Response To Antibiotics Underlies Suppressive Drug Interactions Semantic Scholar




Carbomycin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology



Spiramycin 1 5million Tablets Rosheta



Mechanisms Of Other Antimicrobial Drugs Microbiology



Q Tbn And9gcth3d8x1nireuodgfhyz04qsitlwdy5u24hqn3wfh7gfdgiknay Usqp Cau




Spiramycin And Azithromycin Safe For Administration To Children Exert Antiviral Activity Against Enterovirus 1 In Vitro And In Vivo Sciencedirect



1
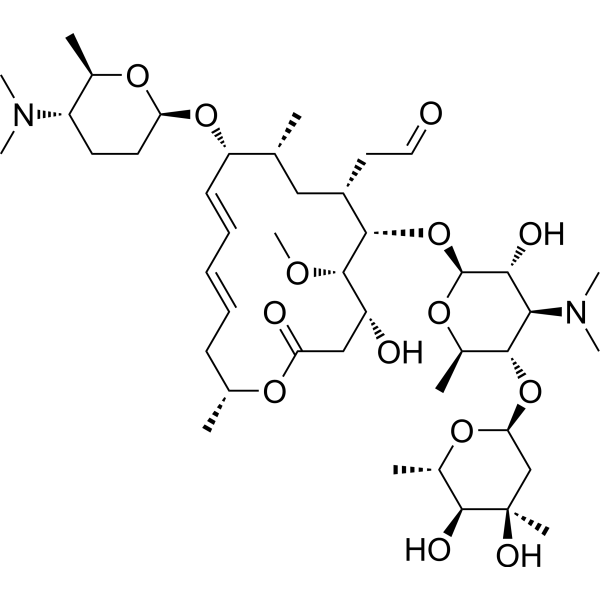



Spiramycin Rovamycin Antibiotic Medchemexpress




Clarithromycin Wikipedia




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



2
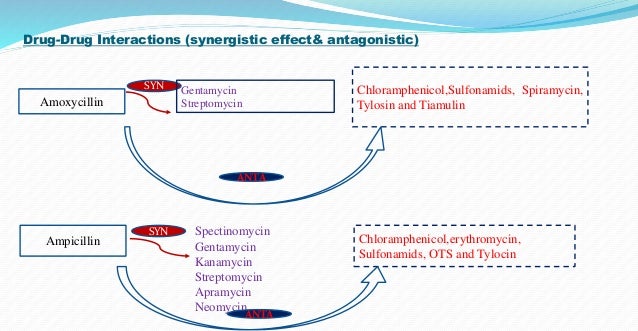



Antibiotics Classification Synergism And Antagonism




Pdf Spiramycin Renaissance
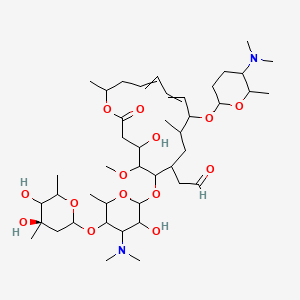



Rovamycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem




Spiramycin Tablets At Rs 1375 Box Gidc Vatwa Ahmedabad Id




Pdf Adsorption Of Metronidazole And Spiramycin By An Algerian Palygorskite Effect Of Modification With Tin
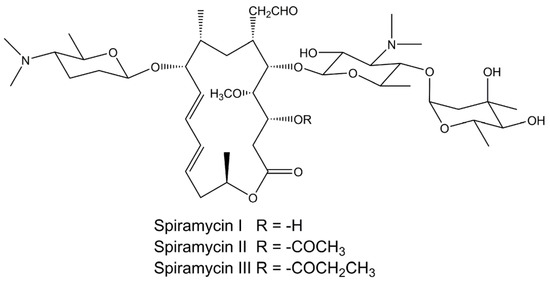



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Congenital Toxoplasmosis What Is The Evidence For Chemoprophylaxis To Prevent Fetal Infection Mandelbrot Prenatal Diagnosis Wiley Online Library
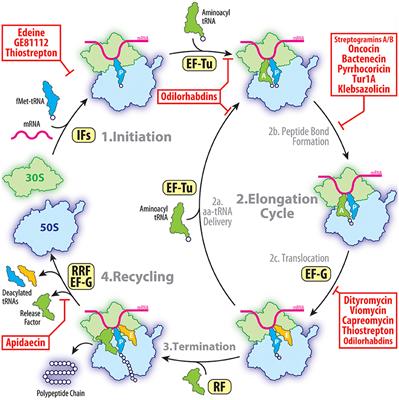



Frontiers The Mechanisms Of Action Of Ribosome Targeting Peptide Antibiotics Molecular Biosciences
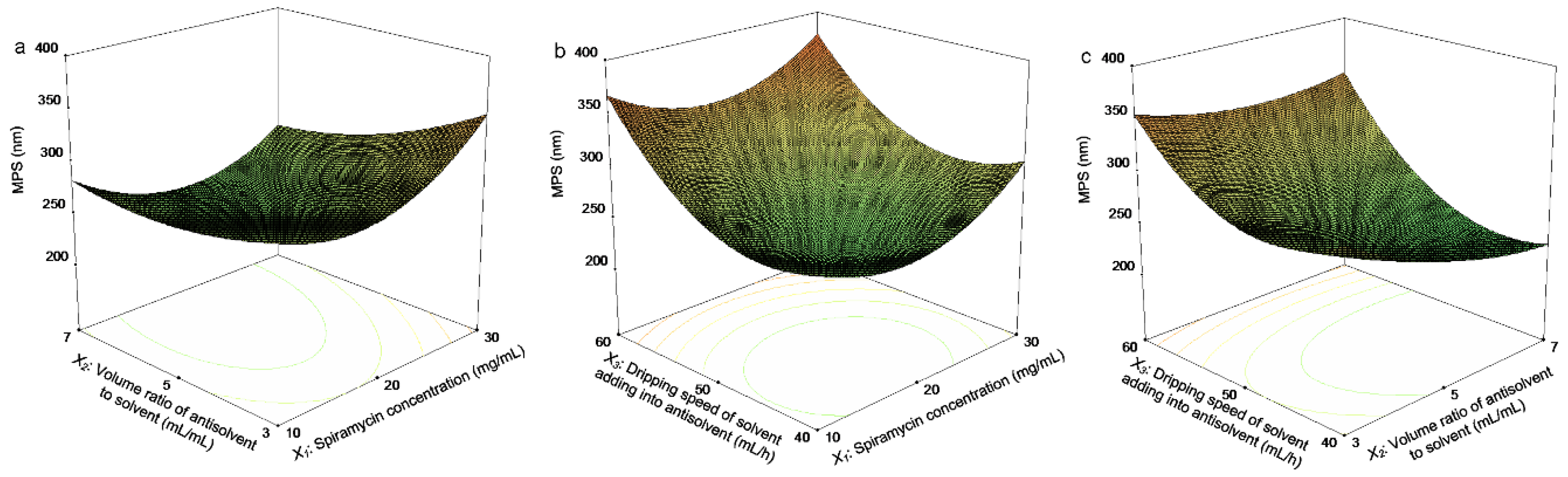



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Successful Treatment Of Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis By Spiramycin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Sciencedirect
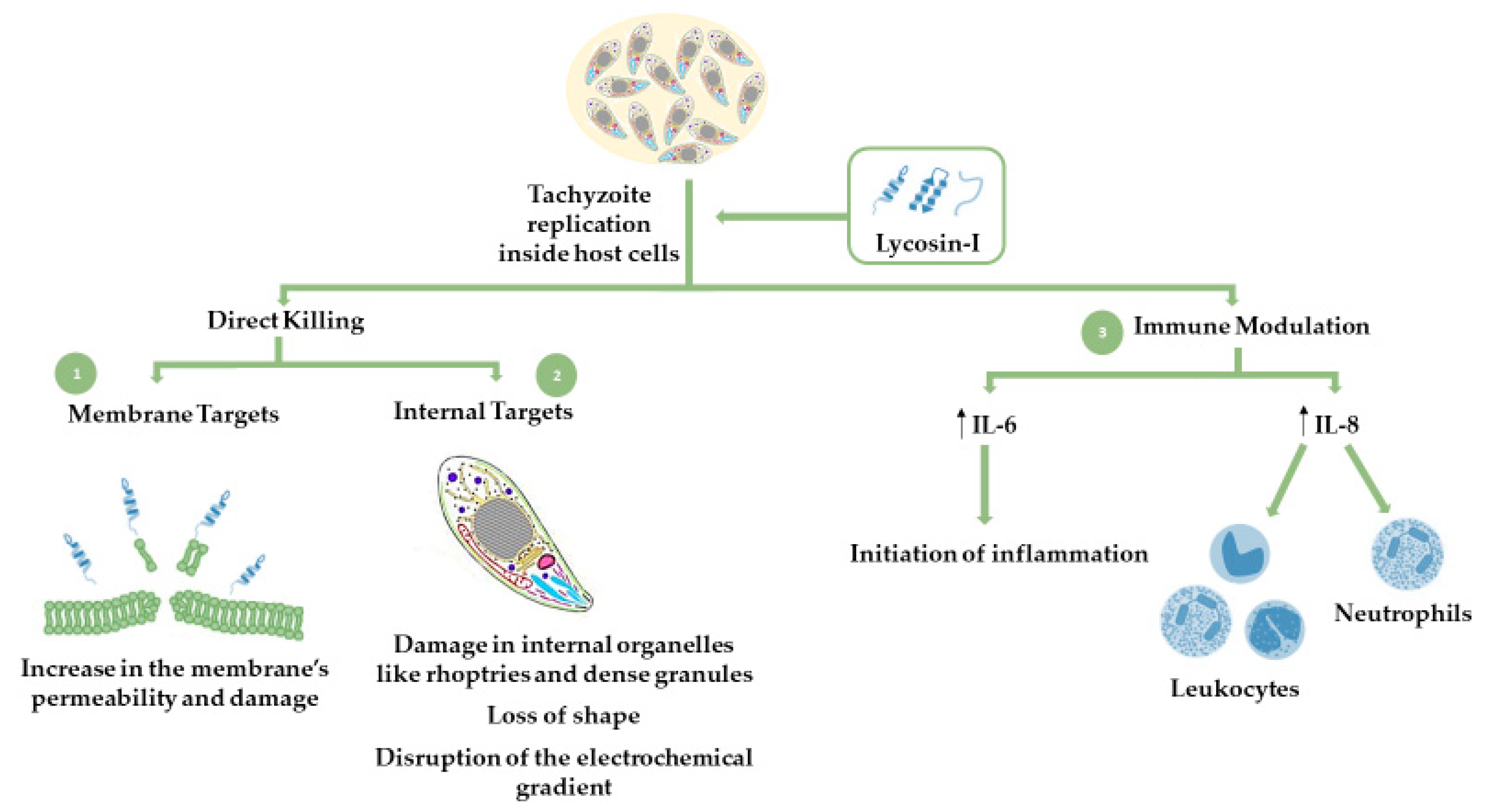



Molecules Free Full Text Antimalarial Agents As Therapeutic Tools Against Toxoplasmosis A Short Bridge Between Two Distant Illnesses Html



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿